RNNoise
RNNoise is a RNN network based noise reduction method, which performs quite well on suppressing environment noises. The idea behind is: adjust the frequency bin (frequency interval is NOT equally spaced) gain to suppress the noise parts of bins dynamically.
In details
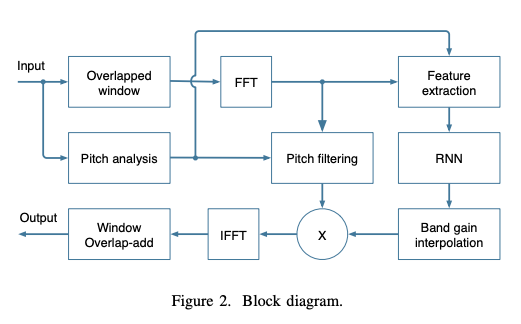
In the diagram above, the most important part is the RNN to esitmate the gain which should be applied to the frequency bin to remove the noise.
The logic behind is that RNN could be used to classify if the frame is noise or not, if it is total noise, it applies full attenuation; if it contains partial noise, it applies a little attenuation.
Nonlinear beamforming
WebRTC released a beamforming algorithm implementation based on ref[2]. In the summary it saids:
Provided are methods and systems for spatially selecting acoustic sources using
a post-processor that consists of a selection of one postfilter from a set of
postfilters, or a cascade of postfilters, where each postfilter is optimal for
a particular scenario. Each postfilter individually is based on optimizing the
gain for each time-frequency bin based on knowledge of (i) a spatial covariance
matrix for the desired Source, (ii) a spatial covariance matrix for the
interfering Sources, and (iii) microphone signals in Some neighborhood of the
current time-frequency bin.
That is to say it has a desired source which is represented by a spatial covariance matrix.
increased nr of mic is not always helping
The lack of robustness in many existing beam forming approaches is generally
most severe for straightforward optimal procedures such as, for example, the
minimum variance distortionless response (MVDR) method or the related
multichannel Wiener filter. In such cases, the low robustness is a direct
consequence of exploiting the design criteria more effectively. While some more
recent approaches reduce beam former robustness problems by explicitly
accounting for the uncertainty in location of the desired and interfering
Sources, these existing systems gen erally require a large number of
microphones for good performance.
The robustness of MVDR is not as good as we expected.
Some thoughts
In webrtc beamforming algorithm, it uses conventional method to design a set of postfilter with predefined gain. Probably we could use RNN on the feature map of microphone signals to estimate the gain which should be applied to remove the unwanted noise/voice.
To reduce the complexity, we could use the spectrum spacing scheme in RNNoise:
We choose to divide the spectrum into the same approximation of the Bark scale
[12] as the Opus codec [13] uses.
Which is total 22 bands.
The gain is estimated based of the multiple microphone feature input.
Network input
The input of the network is the micrphone signal features and the stearing directon of voice. The output is the gain of total 22 bands.
References
[1] https://jmvalin.ca/papers/rnnoise_mmsp2018.pdf [2] https://patentimages.storage.googleapis.com/ff/00/38/20745bddbee117/US9502021.pdf